IRA recharacterization allows you to transfer funds between Traditional and Roth IRAs in order to optimize tax advantages according to your financial circumstances. This strategy can be beneficial if your income varies, giving you the opportunity to contribute to a Roth IRA during periods of lower income or avoid penalties for surpassing contribution limits. To recharacterize, get in touch with your IRA custodian, indicate the amount and type of recharacterization, and ensure you complete the process by the tax-filing deadline. It is crucial to calculate your net income attributable (NIA) accurately, so make sure to adhere to IRS guidelines. For more information on strategic considerations, refer to the details provided below.
Key Takeaways
- IRA recharacterization allows switching between Traditional and Roth IRAs to optimize tax benefits based on income changes and market conditions.
- Consider recharacterization if you exceed Roth IRA income limits or experience a decrease in income eligibility.
- The recharacterization process requires contacting your IRA custodian and calculating Net Income Attributable (NIA) by the tax-filing deadline.
- Complete IRS Form 8606 and maintain thorough documentation of transactions to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
- Strategic recharacterization can help avoid excess contribution penalties and enhance long-term retirement savings potential.
What Is IRA Recharacterization?

IRA recharacterization is a process that lets you switch your IRA contributions between Traditional and Roth IRAs, helping you maximize your tax benefits based on your current financial situation.
If you find that your initial contributions don't align with your long-term financial goals, recharacterization allows you to transfer funds from one type of account to another, adjusting your Roth IRA contributions or traditional IRA contributions accordingly.
This process can also be beneficial for those considering diversification of retirement portfolios as it provides flexibility in managing tax implications and investment strategies.
To execute this process, you'll need to transfer not just the contributed funds but also any net income attributable (NIA) from your original IRA to the new account type.
It's essential to follow IRS guidelines for accurate calculations. You must complete the recharacterization by the federal tax filing deadline, usually April 15, or by October 15 if you've filed for an extension with Form 4868.
Keep in mind that you'll need a separate IRA account for this process.
If your accounts are at different financial institutions, clear communication between custodians is important.
Benefits of Recharacterization

Recharacterization offers a range of benefits that can enhance your retirement strategy. By allowing you to switch contributions between a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA, you can optimize your tax benefits based on your current financial situation.
Additionally, exploring precious metal investment options can provide a diversified approach to your retirement portfolio. Here are three key advantages:
- Avoid Penalties: If you've exceeded the IRS contribution limits, recharacterization lets you adjust your contributions without incurring a 6% penalty.
- Tax-Free Withdrawals: If you anticipate being in a higher tax bracket in retirement, converting to a Roth IRA can provide tax-free withdrawals, maximizing your income when you need it most.
- Flexibility: Market conditions change, and recharacterization offers the flexibility to switch back to a Traditional IRA if a Roth conversion results in a loss, helping you minimize tax implications.
For 2024, you can contribute up to $7,000 to your IRAs ($8,000 if you're 50 or older).
Recharacterization allows you to strategically adjust contributions, ensuring you make the most out of your retirement savings. Embracing these benefits can greatly impact your long-term financial health.
When to Consider Recharacterization

Understanding when to contemplate recharacterization can greatly impact your retirement planning. You should consider recharacterizing if your income has decreased, making you eligible for Roth IRA contributions after initially contributing to a traditional IRA.
If your contributions to a Roth IRA exceed income limits for tax-free withdrawals, recharacterizing to a traditional IRA can help you avoid penalties. Additionally, incorporating assets like a Gold IRA can provide diversification and act as a hedge against inflation during uncertain economic times, potentially influencing your recharacterization strategy as you balance your investment options with diversifying retirement portfolios.
Market downturns also present a unique opportunity. If you're facing losses in your Roth IRA, you might opt to recharacterize to a traditional IRA, allowing you to defer taxes until your investments recover.
Additionally, if you've made a non-deductible traditional IRA contribution because of your participation in an employer-sponsored plan, recharacterizing to a Roth IRA can enable tax-free growth on those contributions.
Lastly, if you anticipate moving into a higher tax bracket in retirement, recharacterization can be a strategic move to adjust your tax strategy based on your changing financial circumstances.
Types of IRA Accounts
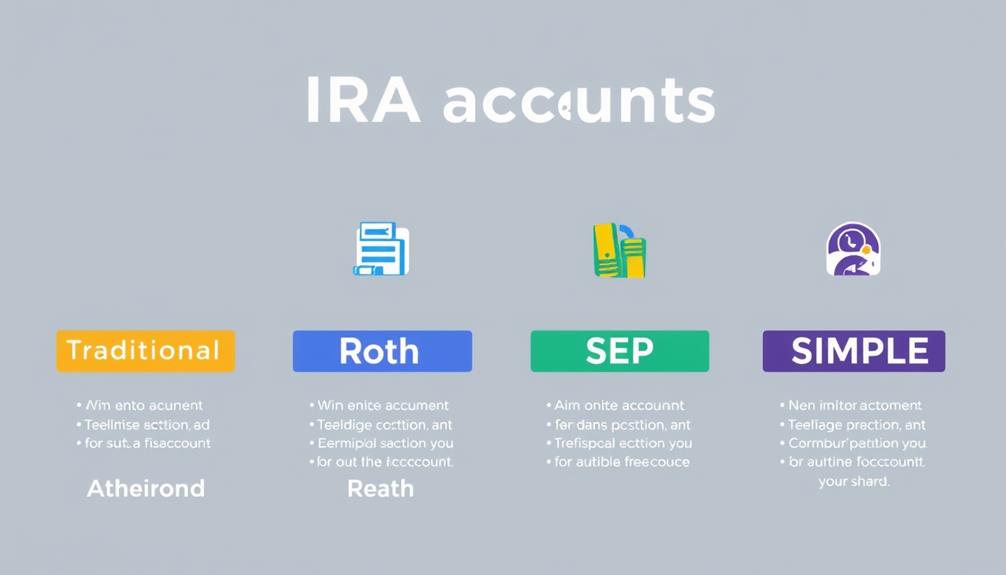
When you're exploring your retirement options, understanding the different types of IRA accounts is essential. A Traditional IRA lets you contribute pre-tax dollars, while a Roth IRA offers tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Additionally, it's important to take into account your investment goals and risk tolerance when choosing the right IRA for you, as this can greatly impact your retirement savings strategy.
If you're self-employed or part of a small business, SEP and SIMPLE IRAs provide unique advantages that can enhance your savings strategy.
Investment Regulations may also play a role in your decision-making process.
Traditional IRA Features
Have you considered the advantages of a Traditional IRA? This retirement account offers several features that can benefit your financial future, especially when it comes to contributions and tax savings.
Here are three key points to keep in mind:
Additionally, a Traditional IRA can serve as a valuable tool for diversifying your retirement portfolio beyond traditional stocks and bonds, which can help protect against market volatility. For those interested in alternative investment options, exploring options like a Gold IRA may also be beneficial.
- Tax-Deductible Contributions: You can make contributions with pre-tax dollars, potentially lowering your taxable income for the year. Depending on your income and whether you participate in an employer-sponsored retirement plan, your contributions might be fully or partially deductible.
- Higher Contribution Limits: For 2024, you can contribute up to $7,000 annually to your Traditional IRA, plus an additional $1,000 if you're aged 50 or older. This allows you to save more as you approach retirement.
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Starting April 1 after you turn 73, you'll need to take RMDs from your Traditional IRA. This guarantees that the funds are eventually withdrawn and taxed, which is important for retirement planning.
Understanding these features can help you maximize your savings and tax advantages while preparing for a secure retirement.
Roth IRA Advantages
While a Traditional IRA offers great benefits, a Roth IRA presents unique advantages that can greatly enhance your retirement strategy. One of the standout features of a Roth IRA is the ability to make tax-free withdrawals in retirement, provided you meet certain conditions. This means your money can grow without the burden of future taxes, making it an attractive long-term savings option.
Additionally, with a Roth IRA, you can enjoy the peace of mind that comes from knowing your investments aren't subject to market volatility as seen in other retirement accounts, such as those involving cryptocurrencies or precious metals avoiding gold IRA scams.
When you make Roth IRA contributions, you're using after-tax dollars, so while you won't get a tax deduction now, you'll enjoy tax-free growth. Plus, unlike traditional IRAs, there are no required minimum distributions (RMDs) during your lifetime. This flexibility allows you to manage your retirement income according to your needs.
In 2024, you can contribute up to $7,000 to a Roth IRA, with an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution if you're 50 or older. However, keep in mind that income limits apply for Roth IRA contributions, starting at $138,000 for single filers and $218,000 for married couples filing jointly.
If you find yourself exceeding these limits, you may consider ways to recharacterize an IRA contribution to take advantage of this valuable retirement account.
SEP and SIMPLE IRAs
SEP and SIMPLE IRAs offer unique retirement savings solutions tailored for small business owners and self-employed individuals.
These accounts provide higher contribution limits compared to traditional and Roth IRAs, allowing you to save more for retirement. Additionally, these accounts can be part of a diversified retirement portfolio, similar to how diversification of retirement portfolio enhances long-term financial security.
Here's what you need to know:
- Contribution Limits: With a SEP IRA, you can contribute up to 25% of your compensation or $66,000 in 2023, whichever is less. SIMPLE IRAs allow a maximum employee contribution of $15,500, plus an extra $3,500 if you're age 50 or over.
- Tax Benefits: Contributions to both SEP and SIMPLE IRAs are made with pre-tax dollars, lowering your taxable income. You'll pay taxes upon withdrawal during retirement.
- Recharacterization Rules: Unlike traditional and Roth IRAs, recharacterization isn't allowed with SEP and SIMPLE IRAs. Once contributions are made, they can't be transferred to another IRA type for tax purposes.
These features make SEP and SIMPLE IRAs attractive options for boosting your retirement savings while enjoying tax advantages.
Make sure to evaluate your business structure and income when choosing the best fit for your retirement planning.
Recharacterization Process

To start the recharacterization process, you'll need to reach out to your IRA custodian and specify the type of recharacterization and the amount involved.
Understanding the tax implications of your decision can be essential, especially if you're also considering your overall financial planning for retirement, which includes evaluating financial considerations for elderly care.
Make sure you have a separate IRA account ready to receive the funds, as well as the necessary documentation to calculate any earnings or losses.
You'll also want to keep in mind the tax-filing deadlines to guarantee a smooth shift.
Steps for Recharacterization
Recharacterizing your IRA can be a straightforward process if you follow the right steps.
Understanding the best ways to earn money online can help you find additional income to contribute to your IRA or assist you during the recharacterization process.
Here's how you can do it effectively:
- Contact Your IRA Custodian: Get in touch with your IRA custodian and inform them that you want to initiate a recharacterization. Specify the type of IRA you want to transfer from and to, along with the amount.
- Calculate Net Income Attributable (NIA): Use IRS Worksheet 1-3 to determine the NIA related to your contribution. This amount is essential to include in your recharacterization.
- Meet the Deadline for Recharacterizing: Confirm that you complete the recharacterization process by the tax-filing deadline, typically April 15.
If you've filed for an extension, you'll have until October 15 to finalize it, avoiding any penalties.
Required Documentation and Forms
Before you initiate the recharacterization process, it's important to gather the necessary documentation and forms.
Start by completing the IRA Recharacterization Form, which indicates your intent to transfer contributions between traditional and Roth IRAs. This form is essential for your recharacterization to be processed correctly. Conducting thorough checks on your financial history can be likened to the importance of background checks employers perform to guarantee a candidate's reliability.
Next, you'll need IRS Form 8606. This form is required for reporting recharacterizations on your federal tax returns, particularly significant if you're doing a partial recharacterization. It helps make sure you comply with tax regulations.
Additionally, your IRA custodian will issue two Form 5498s for the recharacterized contributions—one for each IRA type involved. These forms detail the contribution amounts and earnings, so keep them handy.
It's also crucial to maintain records of all documentation, including transaction confirmations and any correspondence with your IRA custodian. This will be helpful for future reference and tax purposes.
Important Deadlines

While steering through the recharacterization of your IRA contributions, it's vital to be aware of key deadlines to avoid penalties. Here are three important dates to keep in mind:
- Tax-Filing Deadline: You must complete the recharacterization by the tax-filing deadline, which is typically April 15. For the tax year 2024, this date is April 15, 2025.
- Extension Deadline: If you file for an extension using IRS Form 4868, your deadline for recharacterization can stretch to October 15, 2025. This gives you additional time to make adjustments.
- Same Tax Year Requirement: Remember that recharacterizations must occur within the same tax year as your original contribution. Failing to adhere to this rule could lead to penalties.
Additionally, don't forget to report your recharacterization using IRS Form 8606 on your tax return. This step is vital for compliance with IRS regulations.
Keeping track of your contribution years accurately will help you navigate the recharacterization process smoothly and avoid unnecessary complications. Stay organized, and you'll manage your IRA effectively!
Earnings Calculation

When calculating earnings for your IRA recharacterization, it's important to follow the IRS guidelines closely to guarantee accuracy. You'll want to utilize IRS Worksheet 1-3, which helps you determine the net income attributable (NIA) to the recharacterized contributions.
Remember, the NIA calculation involves the total earnings or losses on your entire IRA balance—not just the specific contribution you're recharacterizing.
If you're performing a partial recharacterization, it's significant to pinpoint the specific earnings that correspond to the amount being moved. This might require assistance from your IRA custodian, as they can provide detailed breakdowns of your account's performance.
As you complete the earnings calculation, keep in mind the IRS requires accurate reporting of any earnings included in the recharacterization. Typically, you'll use IRS Form 8606 for this purpose.
Completing your earnings calculation by the applicable tax deadlines is critical to guarantee compliance and avoid penalties related to excess contributions. Staying organized and informed will make the recharacterization process smoother, and help you manage your IRA effectively.
Tax Reporting Requirements

When you recharacterize your IRA contributions, you need to be aware of the specific reporting requirements to stay compliant.
You'll have to fill out IRS Form 8606 and may receive multiple Form 5498s from your financial institution.
Accurate reporting is essential to avoid potential penalties and guarantee your tax calculations are correct.
Reporting Forms Required
Have you considered how to properly report your IRA recharacterizations? Understanding the reporting forms required is vital for compliance with IRS guidelines. Here's what you need to know:
- IRS Form 5498: This form reports your IRA contributions, including any recharacterizations. It's issued by your IRA custodian to both you and the IRS.
- Form 1099-R: This form is required for reporting distributions from your retirement accounts, including recharacterizations. It includes specific codes to clarify the nature of the transaction.
- IRS Form 8606: If you perform a partial recharacterization, you need to file this form with your tax return. Full recharacterizations don't require it.
Make sure you accurately calculate the net income attributable (NIA) to your contribution being recharacterized, as this must be included in your total report.
Thorough documentation is essential to avoid complications with the IRS. By following these steps and utilizing the correct forms, you can guarantee a smooth recharacterization process and remain in good standing with the IRS.
Key Deadlines to Remember
To secure you meet your tax obligations, it's important to keep key deadlines for IRA recharacterizations in mind. The deadline for recharacterizing your IRA contributions aligns with the tax-filing deadline, which is typically April 15. For contributions made in 2024, this deadline extends to April 15, 2025.
If you file for an extension using IRS Form 4868, you can push the recharacterization deadline to October 15, 2025. Completing the recharacterization process before the tax-filing deadline is vital to avoid penalties for excess contributions.
If you're recharacterizing partial contributions, make sure you accurately calculate the net income attributable (NIA) to stay compliant with IRS regulations. Once you've completed the recharacterization, you'll need to report it on your federal tax returns using IRS Form 8606.
This form documents your recharacterization and guarantees that you're following IRS guidelines properly. Remember, staying on top of these deadlines can save you from unnecessary hassles and penalties come tax season.
Importance of Accurate Reporting
Accurate reporting of IRA recharacterizations is essential for compliance with IRS regulations and to steer clear of potential penalties. When you recharacterize your contributions, you need to follow specific tax reporting requirements to guarantee everything is documented properly.
Here are three key points to keep in mind:
- Forms Required: You must file IRS Form 8606 for partial recharacterizations and IRS Form 5498 for documenting both the original and recharacterized contributions.
- Earnings and Losses: Calculate and report any earnings or losses associated with your recharacterized contributions accurately. This follows the IRS guidelines to determine the net income attributable (NIA) to your contributions.
- Record Keeping: Maintain thorough records of all your recharacterization transactions. This substantiates your tax filings and provides necessary documentation if the IRS requests it.
Failing to report your recharacterization can lead to discrepancies that may invite IRS inquiries or penalties.
Common Scenarios for Recharacterization

Recharacterization can be a strategic move in various situations, particularly when your financial circumstances change. For instance, if your income exceeds the Roth contribution limits, you might choose to recharacterize your contribution from a Roth to a Traditional IRA. This allows you to claim a tax deduction in the current year, providing immediate financial relief.
Alternatively, if you initially made a non-deductible contribution to a Traditional IRA, but later realize you qualify for Roth benefits, recharacterization lets you switch to a Roth IRA. This adjustment can optimize your tax strategy and enhance your long-term savings potential.
High-income earners who experience a temporary drop in income can also benefit from recharacterization. By switching from Traditional IRA contributions to Roth, you can take advantage of lower tax rates during that period.
If you accidentally over-contribute to your IRA, recharacterization within the deadline is essential to avoid the 6% penalty on excess contributions.
Strategic Considerations

Steering the decision to recharacterize your IRA requires careful thought of several strategic factors. Recharacterization can optimize your tax outcomes, particularly as your income levels change or when market conditions fluctuate.
Here are three important aspects to take into account:
- Income Levels: If your income surpasses the limits for Roth contributions, switching from a Roth IRA to a Traditional IRA could be beneficial.
- Market Conditions: Evaluating the market is essential. If asset values are declining, converting to a Roth IRA now can lock in lower taxes on future gains.
- Tax Implications: Carefully calculate the net income attributable (NIA) during the recharacterization process, since this can greatly affect your overall tax liability and the amount transferred between IRA types.
Timing also plays a significant role. Confirm you complete any recharacterizations by the tax-filing deadline (April 15) or the extended deadline (October 15) to avoid penalties.
Frequently Asked Questions
When Must an IRA Recharacterization Be Completed By?
You must complete an IRA recharacterization by the tax-filing deadline, usually April 15 of the following year. If you file an extension, the deadline extends to October 15, but you need to act timely.
How Do I File an IRA Recharacterization?
Filing an IRA recharacterization's as easy as pie! Just notify your custodian about your desired contribution shift, complete necessary forms, and remember to meet the deadlines. Keep records for accurate tax reporting—it's essential!
Do I Need to Amend My Tax Return for Recharacterization?
Yes, you might need to amend your tax return for recharacterization. If you recharacterize after filing, file IRS Form 1040-X to correct any contributions or deductions. It's best to consult a tax professional for guidance.
How to Calculate Recharacterization Amount?
Did you know that nearly 30% of IRA owners consider recharacterization? To calculate the recharacterization amount, total your contributions, account for earnings or losses, and apply the IRS formula accurately before your tax deadline.
Conclusion
To summarize, IRA recharacterization can be a smart strategy to safeguard your savings and optimize your tax situation. By understanding the benefits and knowing when to act, you can navigate the nuances of your accounts with confidence. Whether you're shifting from a traditional to a Roth IRA or vice versa, making informed decisions can lead to financial freedom. So, stay savvy, strategize your steps, and seize the potential of your retirement resources!
Helen brings a wealth of experience in investment strategy and a deep passion for helping individuals achieve their retirement goals. With a keen understanding of market dynamics, Helen has been instrumental in shaping the vision and direction of Gold IRA Markets. She specializes in creating innovative solutions that align with our clients’ long-term investment objectives.